 Strategic Reward Management
Strategic Reward Management 
Introduction
Strategic reward management refers to the procedure of development, design, and implementation of a scheme to reinforce and support anticipated behavior in an organization. It is the process of formulating and implementing guiding principles, philosophies, and strategies of rewards. The decision that the management makes gives a clear outline the organization will utilize to enhance productivity through rewards in the future, and how the rewards will be administered effectively. The British Airways is the largest airline in the Great Britain worth 52,000 employees. It has a strategic management that links to its business strategies. It has eight principles that ensure the employees remain motivated. In the current business environment that is characterized by stiff competition, strategic reward management is very significant. It helps the human resource management and the management in general to think of effective ways of using rewards to motivate the employees so that they can work together towards achieving the organizational goals. Strategic reward management should be utilized even during recession when the business cycle slows down. During recession, the business has to struggle to maintain customers and its reputation for it to rise again.
Thus, customer motivation is crucial; hence the reward strategy is vital. Organizations require proper property management to ensure the employees have the right space and equipment to perform their duties. In this case, property management system (PMS) is a key factor in strategic reward management. Pay costs and other expenses in an organization have to be considered when adding another item in the budget that requires finances. Thus, Management Accounting System (MAS) must be considered properly to ensure the strategic reward program is executed effectively. A simple practice such as offering coffee to the employees makes them feel appreciated. Embracing a Kopi Gank culture works wonders in organizations. Even if the British Airline has succeeded in its strategic reward system, there are recommendations that can make it more excellent. Strategic reward management requires keen consideration during recession, in its property management system (PMS), Management Accounting System (MAS), and a positive simple culture such as Kopi Gank culture to maintain a motivated team of employees and achieve organizational goals.
Recession
British Airways has not escaped the recent economy recession that has affected many parts of the world. The company was founded in 1974 by the national government, but was privatized in 1987. It has enough experience in the field, but it cannot evade the recession that is affecting all other parts of the world. As an international transport company, BA has faced recession that has negatively affected it in several ways. There has been inflation in the world, with petroleum products that the company uses being the most affected. The prices of petroleum products have been unstable, making products and services to fall and rise without prior warning. The transportation industry is directly affected by the recession in the world, thus making British Airway among the most affected companies because of its size, complexity and international image. For instance, the company made a profit of £8002 million in 2001. However, in 2002, it experienced a net loss of £516 million as a result of the recession in the world. Similarly, in 2004, the company operated with £883 million profit, which was followed by £397 million loss in 2005. This indicated that the company, like many other organizations in the world, is suffering from recession. As a result of the recession, BA adopted a strategic reward management that would ensure that its employees remain motivated so that they work with the right morale, treat customer properly and help the organization recover. The BA Strategic Reward Structure can be summarized in Figure 1.
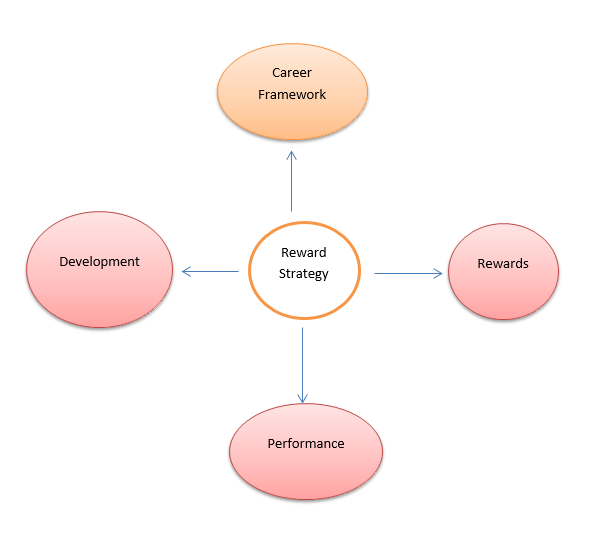
Figure 1: British Airways Reward System Summary
The reward system consists of both the financial and employees benefit. Apart from benefiting financially, the employees are equipped so that they can treat the customer with utmost care. The two elements form the total remuneration that enhances production at the work place. On the same note, the reward system has the non-financial components which include personal growth, responsibility, recognition, achievement and praise. The British Airways management understood that the financial aspects could not achieve the desirable goals during recession. In this case, the organization focused on increasing the non-financial components so as to reduce the cost during recession.
The decision of British Airways was informed by the Expectancy Theory. According to this theory, employees must work extra hard for them to gain a salary increases. In this case, BA sets targets for every employee. Those who worked smartly managed to achieve the target and go beyond the set standards. They worked extra hours and gave their work the commitment it deserves. They served the customers with respect so that the company could continue making profits and give them the rewards. The company applied the three major factors in the expectancy theory which are valence, instrumentality and expectancy to ensure that it did not sink in recession.
Are you interested in our Strategic Reward Management paper? Click the button and download pdf sample to read full version of this paper.






